2020-07-30
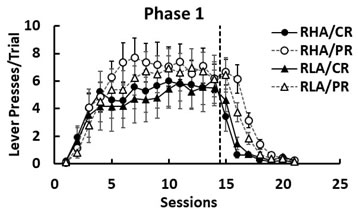
Individuals trained under partial reinforcement (PR) typically show a greater resistance to extinction than individuals exposed to continuous reinforcement (CR). This phenomenon is referred to as the PR extinction effect (PREE) and is interpreted as a consequence of uncertainty-induced frustration counterconditioning. In this study, we assessed the effects of PR and CR in acquisition and extinction in two strains of rats, the inbred Roman high- and low-avoidance (RHA and RLA, respectively) rats. These two strains mainly differ in the expression of anxiety, the RLA rats showing more anxiety-related behaviors (hence, more sensitive to frustration) than the RHA rats. At a neurobiological level, mild stress is known to elevate corticosterone in RLA rats and dopamine in RHA rats. We tested four groups of rats (RHA/CR, RHA/PR, RLA/CR, and RLA/PR) in two successive acquisition-extinction phases to try to consolidate the behavioral effects. Animals received training in a Pavlovian autoshaping procedure with retractable levers as the conditioned stimulus, food pellets as the unconditioned stimulus, and lever presses as the conditioned response. In Phase 1, we observed a PREE in lever pressing in both strains, but this effect was larger and longer lasting in RHA/PR than in RLA/PR rats. In Phase 2, reacquisition was fast and the PREE persisted in both strains, although the two PR groups no longer differed in lever pressing. The results are discussed in terms of frustration theory and of uncertainty-induced sensitization of dopaminergic neurons.

Individuals trained under partial reinforcement (PR) typically show a greater resistance to extinction than individuals exposed to continuous reinforcement (CR). This phenomenon is referred to as the PR extinction effect (PREE) and is interpreted as a consequence of uncertainty-induced frustration counterconditioning. In this study, we assessed the effects of PR and CR in acquisition and extinction in two strains of rats, the inbred Roman high- and low-avoidance (RHA and RLA, respectively) rats. These two strains mainly differ in the expression of anxiety, the RLA rats showing more anxiety-related behaviors (hence, more sensitive to frustration) than the RHA rats. At a neurobiological level, mild stress is known to elevate corticosterone in RLA rats and dopamine in RHA rats. We tested four groups of rats (RHA/CR, RHA/PR, RLA/CR, and RLA/PR) in two successive acquisition-extinction phases to try to consolidate the behavioral effects. Animals received training in a Pavlovian autoshaping procedure with retractable levers as the conditioned stimulus, food pellets as the unconditioned stimulus, and lever presses as the conditioned response. In Phase 1, we observed a PREE in lever pressing in both strains, but this effect was larger and longer lasting in RHA/PR than in RLA/PR rats. In Phase 2, reacquisition was fast and the PREE persisted in both strains, although the two PR groups no longer differed in lever pressing. The results are discussed in terms of frustration theory and of uncertainty-induced sensitization of dopaminergic neurons.